Table of Contents
Importance of Cyber Security: Safeguarding the Digital Frontier
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity technology has become paramount. It’s not just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental necessity for organizations of all sizes and across all industries. The digital age has ushered digital security with remarkable technological advances, enabling unprecedented connectivity, efficiency, and innovation. However, it has also brought forth new challenges and risks, making cybersecurity technology more crucial than ever before.
Understanding Cybersecurity Technology
Cybersecurity, often referred to as information security, encompasses a wide range of practices, technologies, and strategies that organizations employ to protect their digital assets from unauthorized access, data breaches, cyberattacks, and other digital threats. It encompasses a multifaceted approach to safeguarding information systems, networks, applications, and data from harm, theft, or compromise.
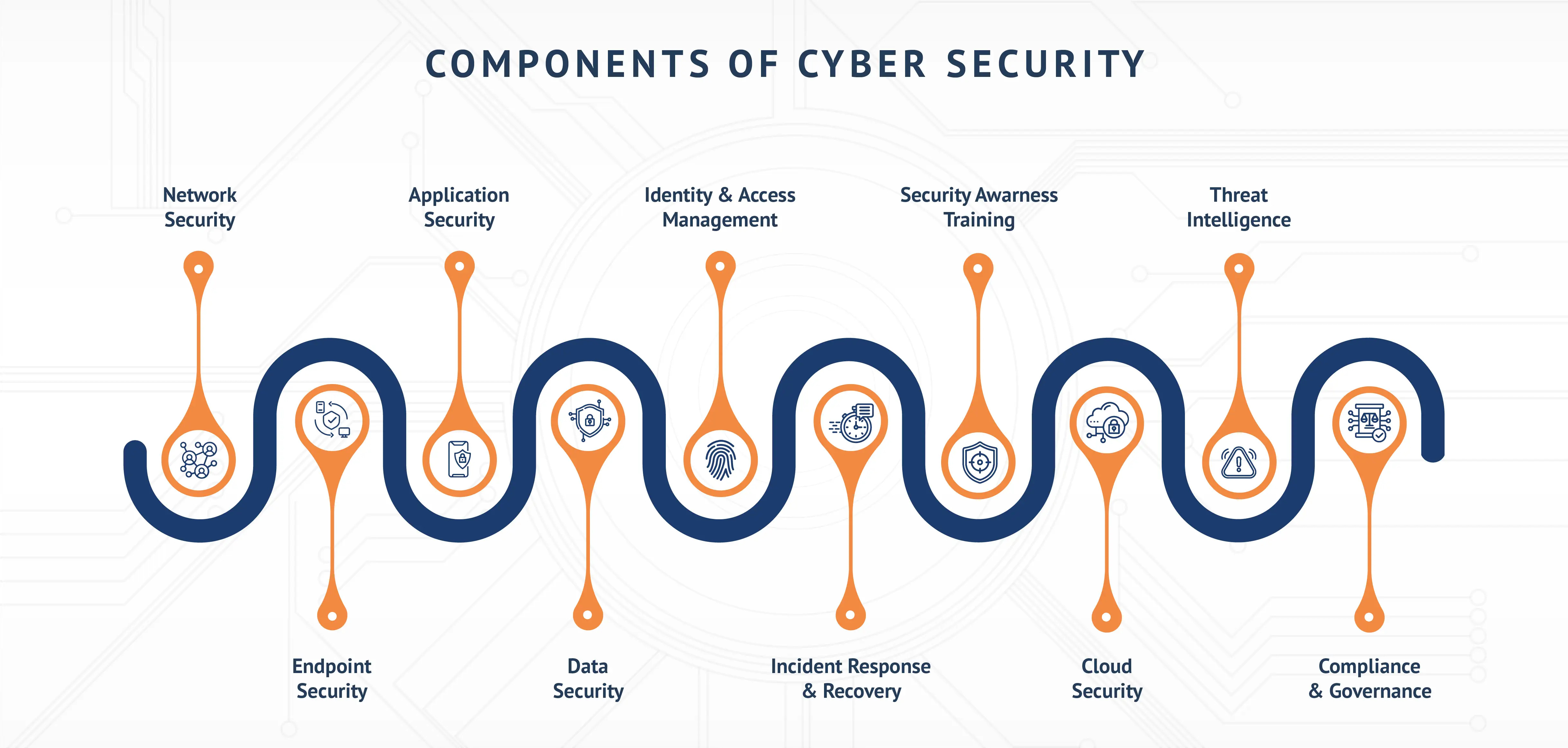
Types of Cyber Security Examples
Cybersecurity isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution; it’s a dynamic and evolving field that adapts to the changing threat landscape. It includes various components, Cyber security examples such as:
- Network Security: Focusing on protecting an organization’s internal network infrastructure and external connections from unauthorised access and cyberattacks.
- Endpoint Security: Securing individual devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets to prevent malware, ransomware, and other threats.
- Application Security: Ensuring that software and applications are developed and configured securely to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive data through encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention measures.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Managing and controlling user access to systems and data, ensuring only authorised individuals have access.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Developing plans and procedures to respond to and recover from security incidents, minimising damage and downtime.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and raising awareness about potential threats.
- Cloud Security: Protecting data and applications hosted in cloud environments, including public, private, and hybrid clouds.
- Threat Intelligence: Monitoring and analyzing the threat landscape to proactively identify and mitigate emerging threats.
- Compliance and Governance: Ensuring that organizations adhere to industry-specific regulations and cybersecurity best practices.
Why is Cyber Security Important?
The importance of cybersecurity to organizations cannot be overstated. Here are compelling reasons why it should be a top priority:
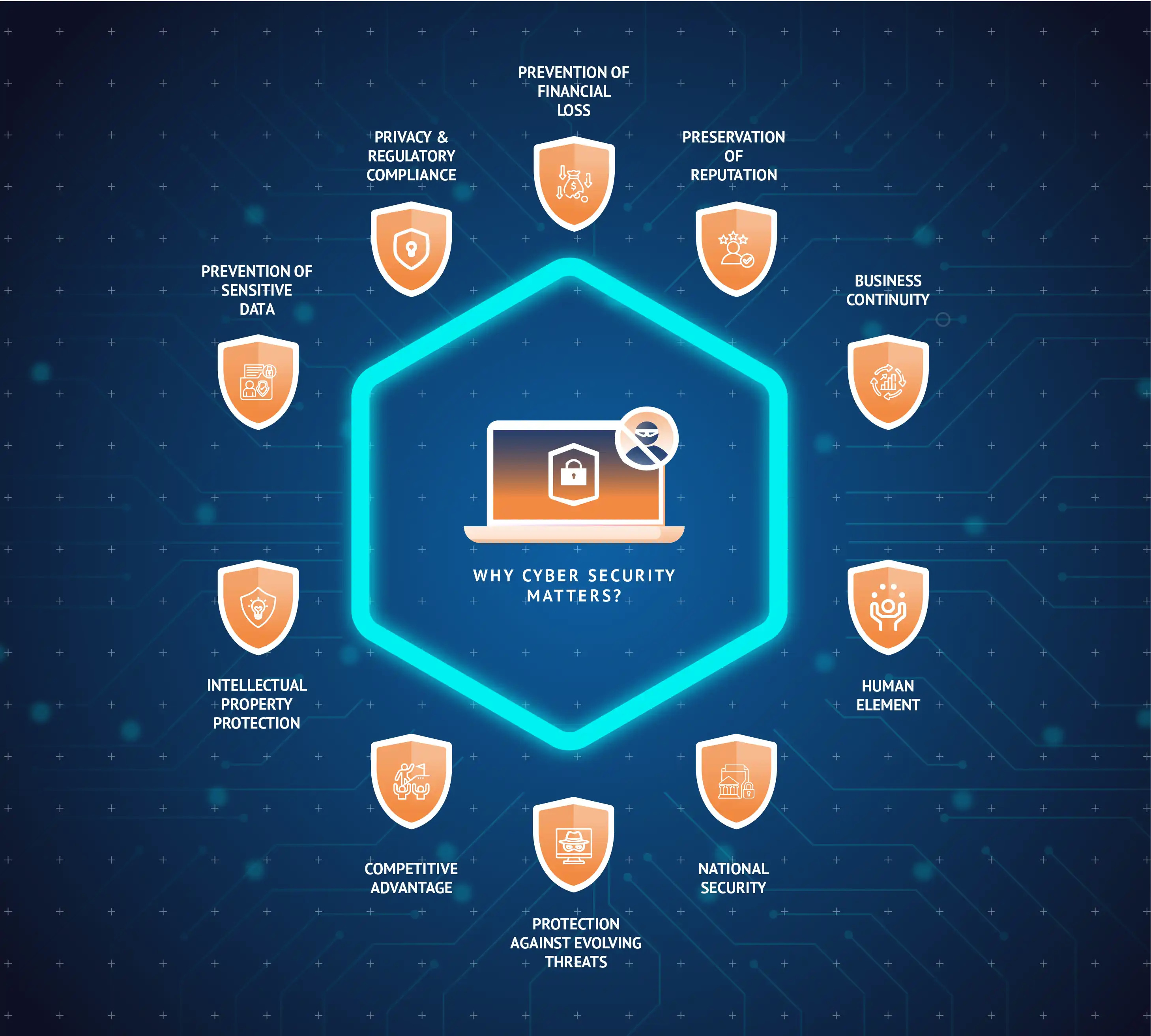
Protection of Sensitive Data
Organizations accumulate vast amounts of sensitive information, including customer data, financial records, intellectual property, and proprietary information. A breach of this data can have catastrophic consequences, including financial losses, legal liabilities, and damage to reputation. Cybersecurity measures are essential to safeguard these valuable assets.
Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
As data privacy regulations become more stringent worldwide (such as the GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California), organizations are legally obligated to protect the personal information they collect and process. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties. Effective cybersecurity practices help ensure regulatory compliance.
Prevention of Financial Loss
Cyberattacks can result in significant financial losses. These losses may arise from direct theft, ransom payments, legal fees, and costs associated with incident response and recovery. Investing in cybersecurity can prevent or mitigate these financial burdens.
Preservation of Reputation
A cybersecurity breach can tarnish an organization’s reputation and erode the trust of customers, partners, and stakeholders. Rebuilding trust can be a challenging and lengthy process, making the prevention of breaches imperative.
Business Continuity
Cyberattacks can disrupt operations, leading to downtime, reduced productivity, and financial losses. Robust cybersecurity measures, including incident response and recovery plans, are critical to maintaining business continuity and minimizing disruptions.
Intellectual Property Protection
For many organizations, intellectual property represents a significant portion of their value. Cybersecurity safeguards protect proprietary designs, patents, copyrights, and trade secrets from theft or compromise.
Competitive Advantage
Demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity can be a competitive advantage. Customers and partners often prefer to work with organizations that prioritize security, viewing them as trustworthy and reliable partners.
Protection Against Evolving Threats
Cyber threats are continually evolving, becoming more sophisticated and diverse. Investing in cybersecurity ensures that an organization is prepared to defend against emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
National Security
In certain industries, such as critical infrastructure and defence, cybersecurity is a matter of national security. Protecting these assets is vital to safeguarding a country’s interests and infrastructure.
Types of cyber attacks
The types of cyber-attacks constantly evolve, shaping the dynamic cyber threat landscape. Cybercriminals and threat actors are continually devising new tactics, techniques, and procedures to breach defenses and exploit vulnerabilities. Some prominent threats include:
- Malware: Malicious software designed to infiltrate systems, steal data, or disrupt operations. Examples include viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware.
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details, often through email or fake websites.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: Overwhelming a target system or network with a flood of traffic, rendering it inaccessible.
- Insider Threats: Threats that originate from within an organization, often involving employees or contractors with malicious intent or negligent behavior.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Long-term, targeted attacks by well-funded and organized adversaries, often associated with nation-state actors.
- Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks that take advantage of previously unknown vulnerabilities, leaving organizations vulnerable until patches are available.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals through psychological manipulation to gain access to systems or sensitive information.
The Human Element
While technology plays a vital role in cybersecurity, human behavior is equally important. Employees are both the first line of defense and a potential vulnerability. Therefore, organizations must prioritize security awareness training and foster a culture of cybersecurity vigilance among their workforce.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is not merely a technical concern; it is an organizational imperative. It is about protecting sensitive data, ensuring compliance, preserving financial stability, and maintaining trust with stakeholders. In today’s digital age, organizations must view cybersecurity as an ongoing process, continuously adapting to the evolving threat landscape. It is an investment in the longevity and resilience of the organization, one that cannot be overlooked or postponed. Organizations that prioritize Cyber Security services are better equipped to navigate the complex and dynamic digital frontier, ensuring their sustained success in an increasingly interconnected world.




